LSA
(Layered Scalable Architecture) is SAP's recommended (reference as a best
practice) approach for modeling (enterprise) data warehouse (EDW) solutions.
Over the years and in line how SAP BW solution was evolving so the LSA
architecture evolved too. There are versions of the LSA for classic
BW 7.x and LSA++ for BW on Hana (BWoH). With an advent of BW for HANA (BW/4HANA) the SAP introduced updated LSA++
architecture too that is sometimes called as integrated layer architecture.
Just
to recap a main differences LSA vs LSA++ lie in: introduction of operational
layer in the LSA++; enabling reporting on aDSO objects of propagation layer; introduction
if virtual layer based on Composite Providers to support virtual data marts; queries
can be directly accessed in SAP HANA database.
Further,
when it comes to LSA++ for SAP BW/4HANA SAP distinguish between:
1/ LSA++ for Simplified Data Warehousing: New BW objects below that
were introduced in LSA++ are further leveraged:
aDSO – object for data standard persistency
Open ODS View - defines reusable BW
data warehouse semantics on field-based structures
Composite Provider - defines virtual
data marts on persistencies (aDSO/InfoObjects) and/or Open ODS views, or a
combination of both
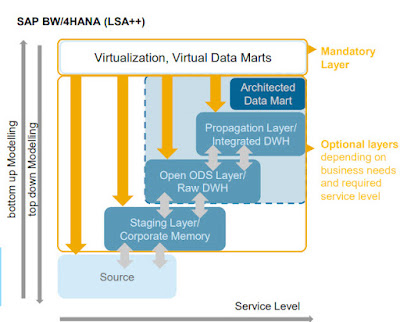
Layers of LSA++
for SAP BW/4HANA:
Operational Data Store – entry layer
on top of which queries can be built
EDW Propagation and Harmonization – provides
semantic an value standardization for data from different sources in highly
harmonized form
Corporate Memory – contains
complete history of loaded data
Architected Data Mart – query access
layers in case query can’t be built already in ODS layer, often case where
additional business logic needs to be put
Virtual Datamart – combines data
from persisted providers (aDSO/InfoObjects) with virtual providers (union,
joins)
2/
LSA++ for Logical Data Warehousing:
In
the simplified data warehouse the data is persistent in one of its layers. This
means data were copied (load or replicated per se) from its source to the DW. Activity
like data copy/move implies a cost. In order to reduce such cost a logical data
warehouse approach comes to a picture. The logical DW attempts to provide a
solution without a need to move the data by acting either as system requesting
or as system providing the data. The logical DW concept allows leveraging of mixed
scenarios in SAP BW.
More
information: